Data Representation
User-defined data types

Non-composite types
- enumerated
TYPE Courses = (English,Chinese,Maths)
- pointer
TYPE SelectParts = ^Parts // It reference the memory location in which the part is stored
Define & Use composite data types
- set, record and class/object
- Pseudocode example of class:
|
|
File organisation and access
Organisation
-
Serial

-
Sequential

-
Random
- Only that the access can be to any record in the file without sequential reading of the file.
- A separate index file is created which has two fields per record.
- The first field has the key field value and the second field has a value for the position of this key field value in the main file.
Access
- Sequential
- Direct
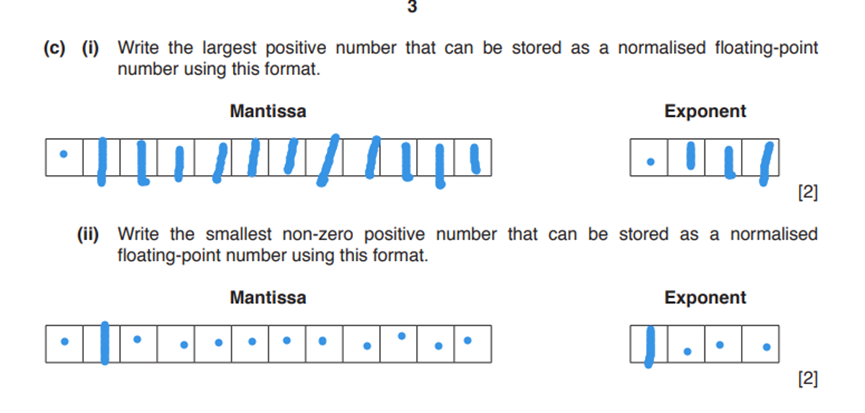
Floating-point numbers, representation and manipulation
- Overflow
- Underflow
- Rounding errors


Communication and internet technologies
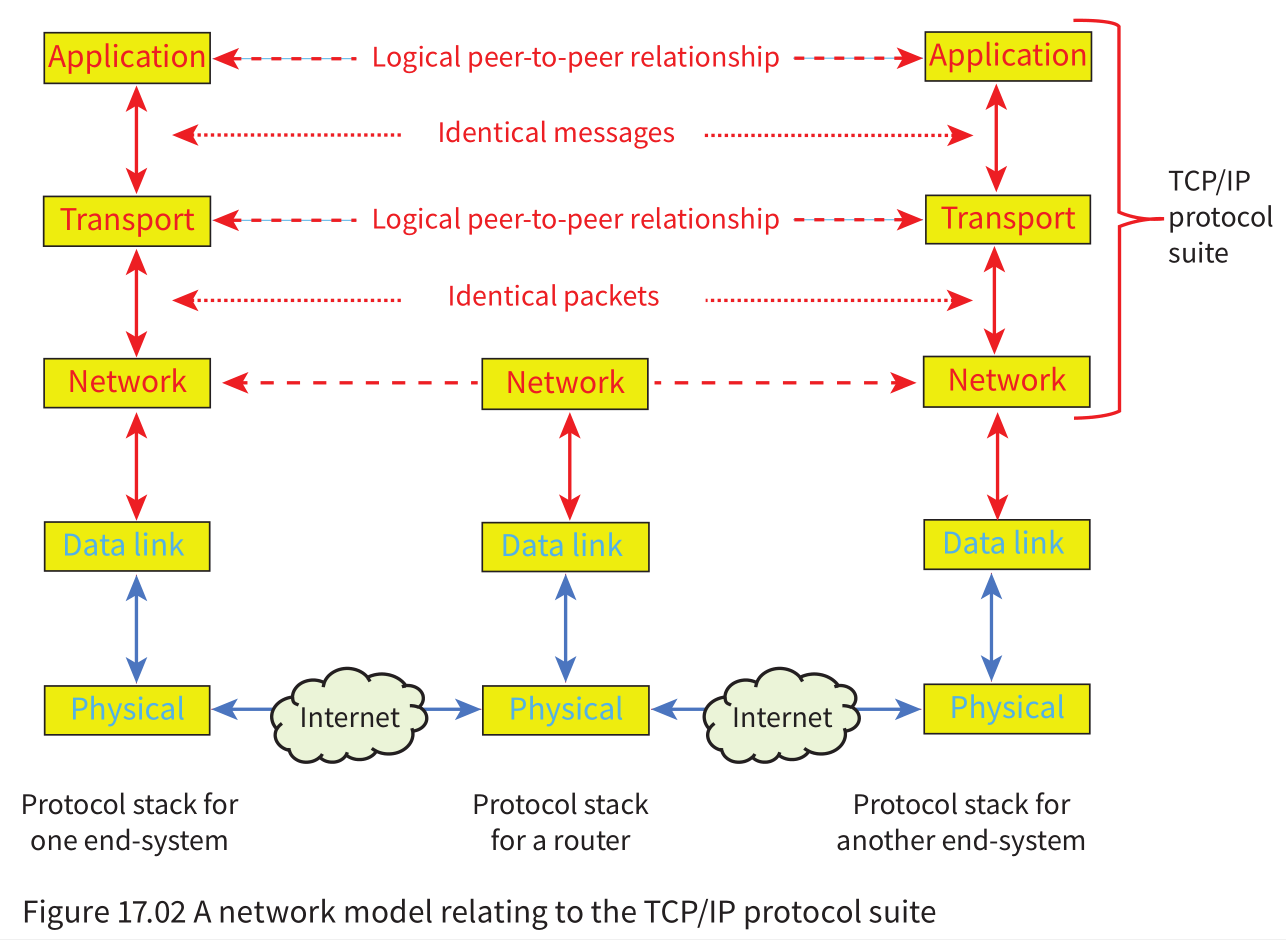
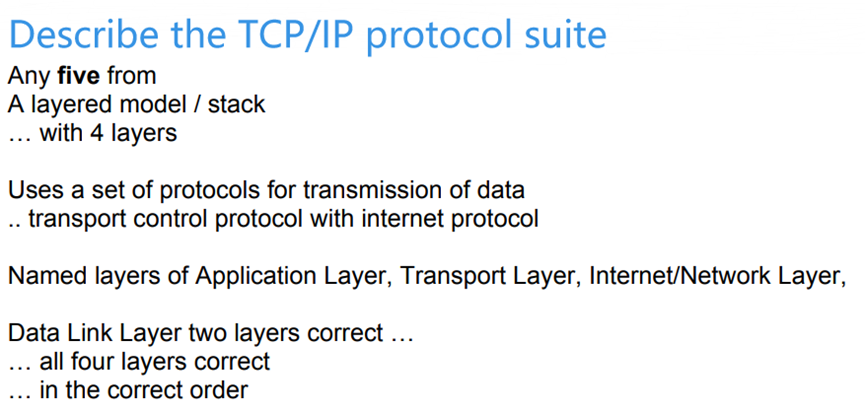
Protocols
Importance

TCP/IP
Bittorrent
- file sharing
- peer-to-peer

Other protocols
- FTP
- IMAP, SMTP, POP3
- HTTP
- ……
Circuit switching, packet switching
Packet

Circuit
- A method of data transfer in which the message is sent over a dedicated communication channel.
Hardware and Virtual Machines
Processors, Parallel Processing and Virtual Machines
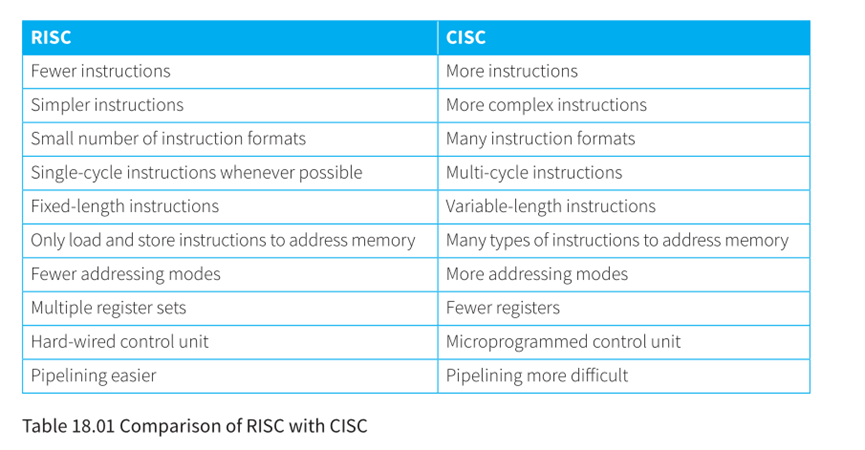
Reduced Instruction Set Computers (RISC)
Complex Instruction Set Computers (CISC)
Parallel processing
- SISD
- SIMD
- MISD
- MIMD

Logic Circuits
Half-adder
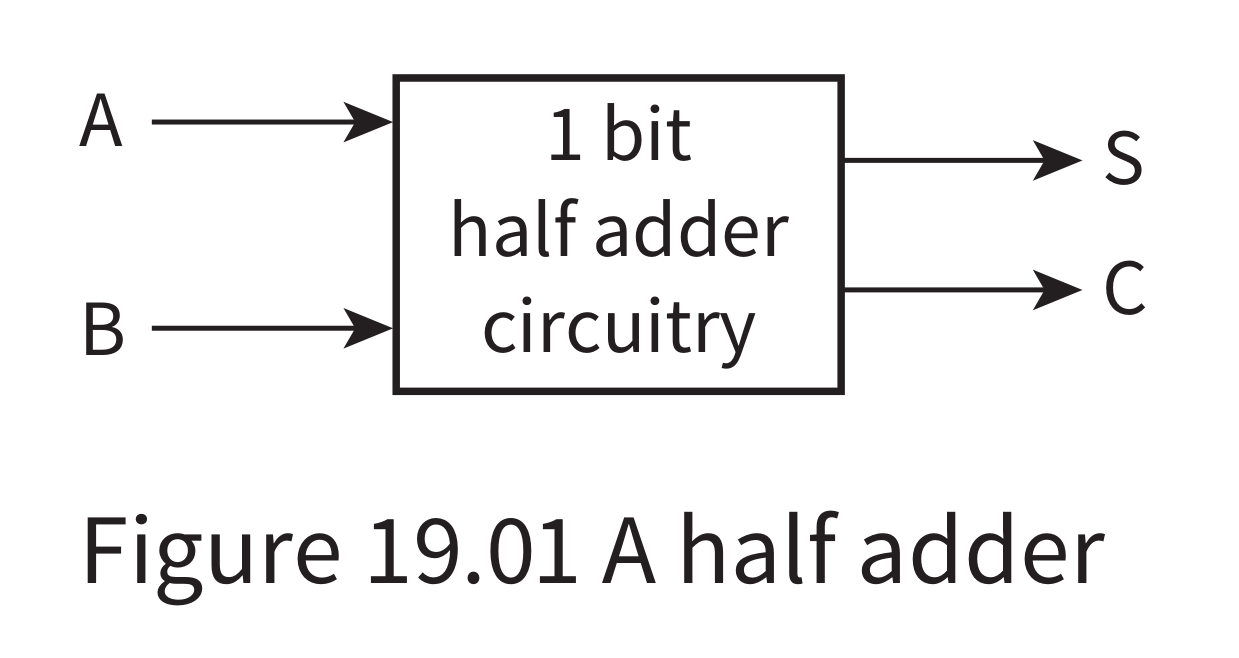
- 2 input
- 2 output
- carry bit
- sum bit
Full-adder
- 3 input
- 2 output
- carry bit
- sum bit
Flip-flop
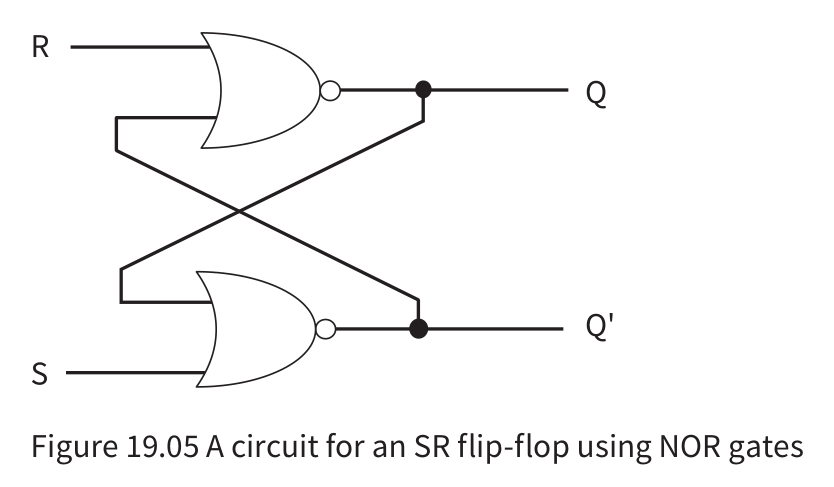
SR
- It can be constructed with two NAND gates or two NOR gates.
- Used as a storage device for 1 bit in the RAM, since it’s values can be altered
- Issue: When the both the input signals are 1 (invalid state) the flip-flop sets the value of Q and Q’ to 0.
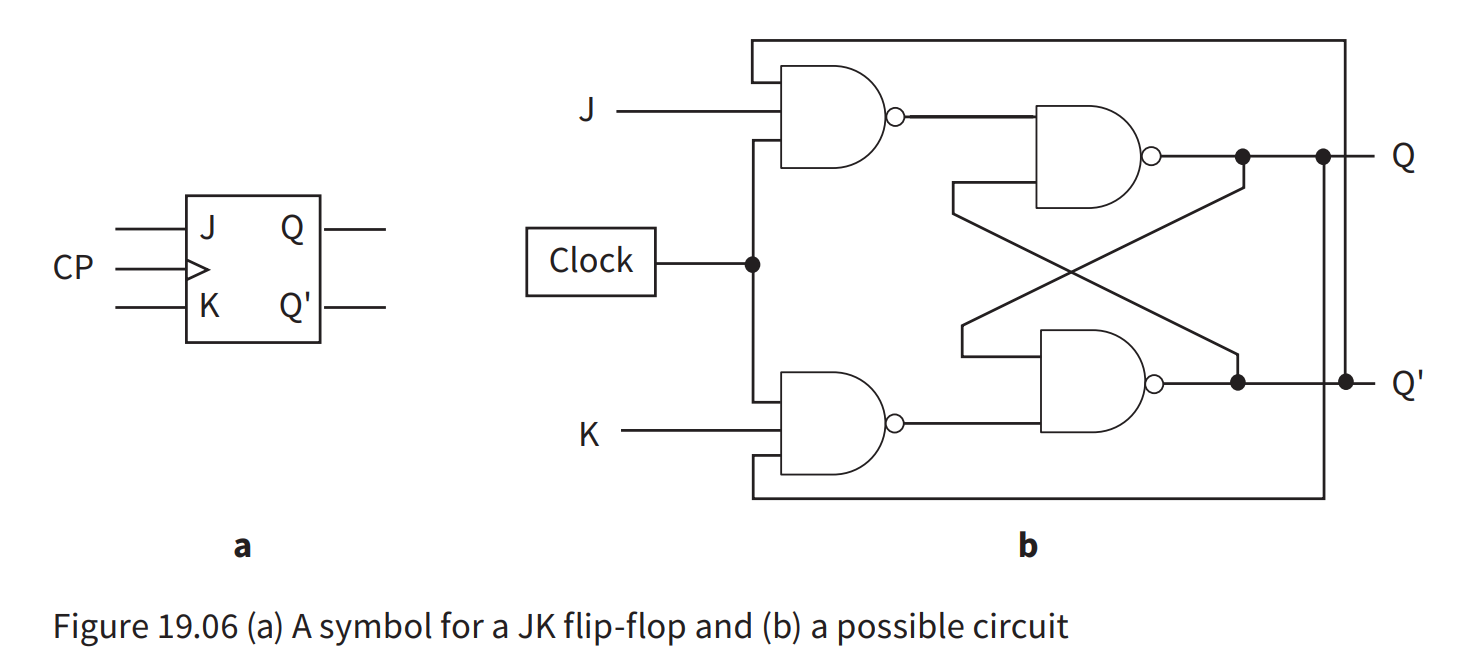
JK
- The J acts as a set input and the K as a clear input.
- There is a clock input to synchronise the inputs.
- When both the input signals are one, Q toggles.
Usage
- Flip-flops are used to build
- Data storage elements
- Digital circuits
Boolean Algebra
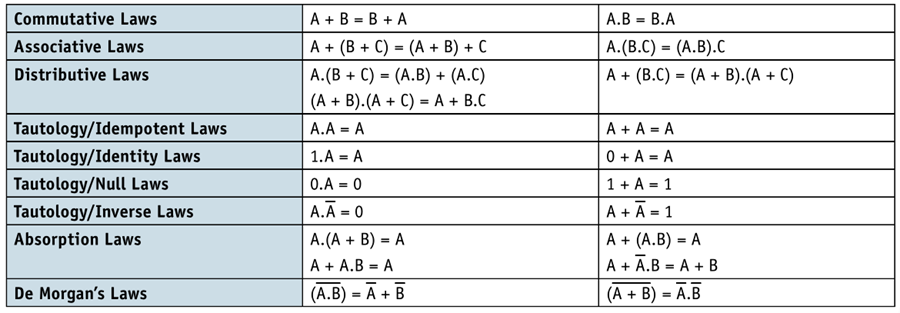
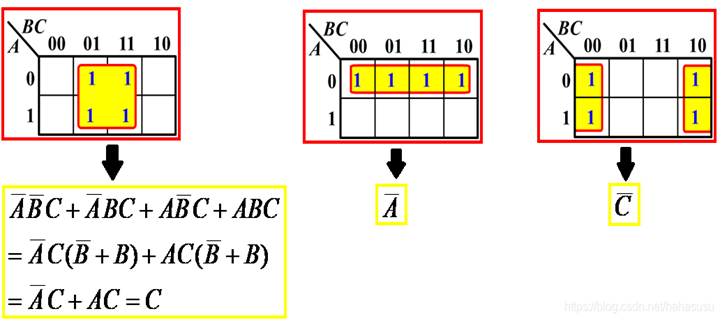
Karnaugh maps
System Software
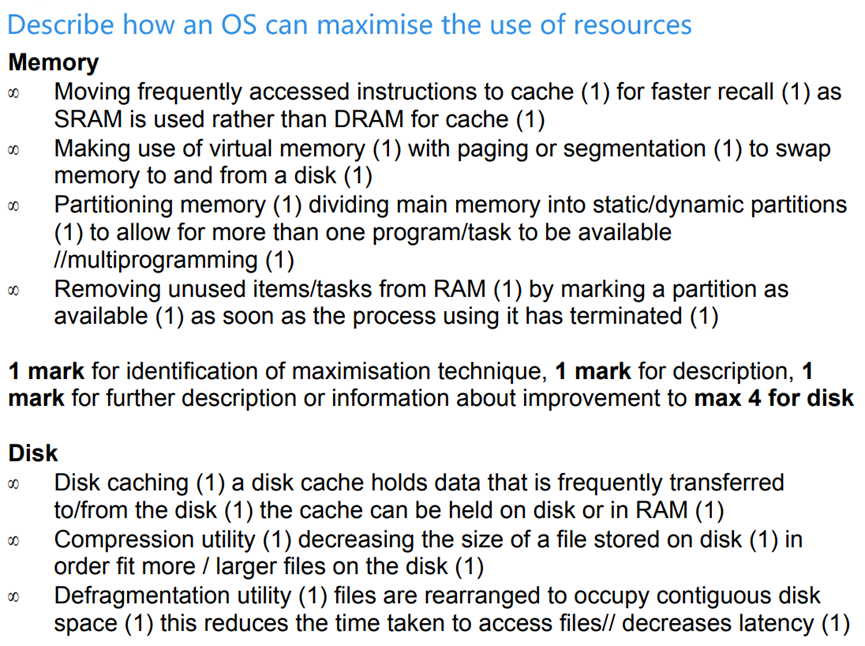
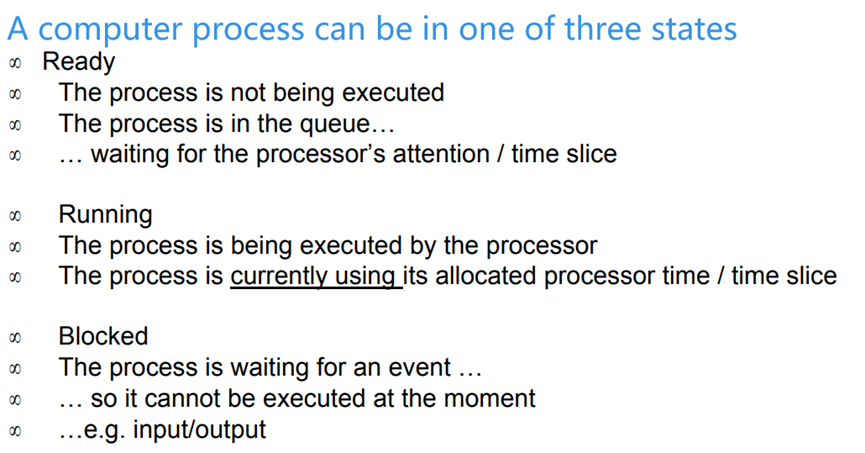
Purposes of an Operating System (OS)
- OS provides utility software, user interface (GUI,CLI), resources management, multi-tasking, a platform to run code……





Translation Software


BNF notation
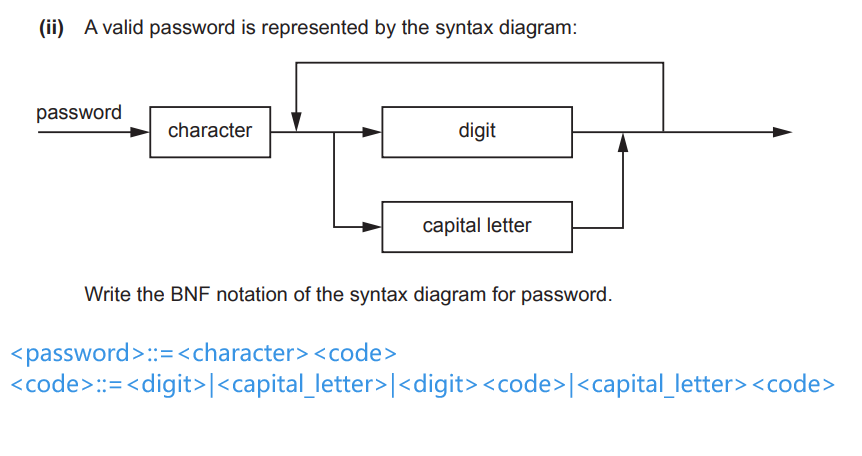
::=|
RPN expression

|
|
Security
Encryption, Encryption Protocols and Digital certificates
- public key, private key, plain text, cipher text, encryption
- symmetric key cryptography and asymmetric key cryptography
Symmetric key encryption


Asymmetric key encryption


Private keys & public key

Digital certificate


Digital signature



Quantum cryptography

SSL & TLS



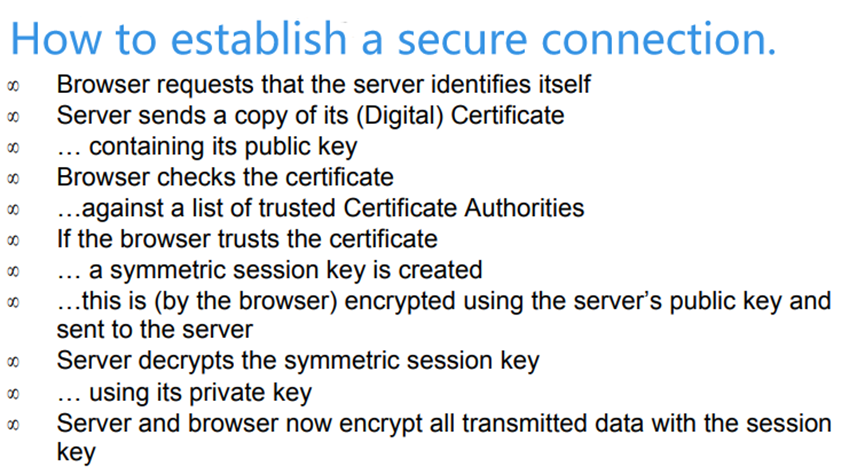
How to establish a secure connection
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Please check the note released before🔗
Computational thinking and problem-solving
Algorithms
Please check the note released before🔗
Recursion


Description
- have a base case
- have a general case
- reach the base case aft er a finite (limited) number of calls to itself.
Benefits
- More elegant
- Use less program code than iterative solutions
Drawbacks
- Large amounts of memory usage and processor time
How to implement recursion (Stack)
- Each time a subroutine is called, a stack frame is pushed onto the stack.
- A stack frame consists of the return address and the values of the local variables.
- When a subroutine completes, the corresponding stack frame is popped off the stack.
Further Programming
Programming Paradigms
- A programming style/classification // characteristics/features that programming language has/uses
Low-level Programming
- Programs use the instruction set of a processor
Addressing mode
- immediate
- direct
- indirect
- indexed
- relative
Imperative Programming (Sequence of commands)

Object Oriented Programming



Declarative Programming (Focus on the result)
- The programmer doesn’t tell the computer what to do. To get information, the programmer poses a query (sets a goal). It’s up to the logic programming system to work out how to get the answer.
- Declarative programming languages include SQL and Prolog.
File Processing and Exception Handling
Record
Pseudocode
|
|
Python3
|
|
File processing
Psedocode
| Structured English | Pseudocode |
|---|---|
| Create a file and open it for writing | OPENFILE <filename> FOR WRITE |
| Open a file in append mode | OPENFILE <filename> FOR APPEND |
| Open a file for reading | OPENFILE <filename> FOR READ |
| Open a file for random access | OPENFILE <filename> FOR RANDOM |
| Close a file | CLOSEFILE <filename> |
| Write a record to a file | PUTRECORD <filename>, <identifier> |
| Read a record from a file | GETRECORD <filename>, <identifier> |
| Move to a specific disk address within the file | SEEK <filename>, <address> |
| Test for end of file | EOF(<filename>) |
Python3
|
|
Recommanded mode parameter
'w'for write'r'for read'a'for append'+'let the file can be read and write at the same time- If the mode is
'w', you cannot usefile.read([size]),file.readline([size])andfile.readlines([sizeint]) - If the mode is
'w+', there is no worry of reading the file
- If the mode is
'b'for open/write/append a binary file- for example:
'wb','wb+'
- for example:
Detail mode parameters
| 模式 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| t | 文本模式 (默认)。 |
| x | 写模式,新建一个文件,如果该文件已存在则会报错。 |
| b | 二进制模式。 |
| + | 打开一个文件进行更新(可读可写)。 |
| r | 以只读方式打开文件。文件的指针将会放在文件的开头。这是默认模式。 |
| rb | 以二进制格式打开一个文件用于只读。文件指针将会放在文件的开头。这是默认模式。一般用于非文本文件如图片等。 |
| r+ | 打开一个文件用于读写。文件指针将会放在文件的开头。 |
| rb+ | 以二进制格式打开一个文件用于读写。文件指针将会放在文件的开头。一般用于非文本文件如图片等。 |
| w | 打开一个文件只用于写入。如果该文件已存在则打开文件,并从开头开始编辑,即原有内容会被删除。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件。 |
| wb | 以二进制格式打开一个文件只用于写入。如果该文件已存在则打开文件,并从开头开始编辑,即原有内容会被删除。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件。一般用于非文本文件如图片等。 |
| w+ | 打开一个文件用于读写。如果该文件已存在则打开文件,并从开头开始编辑,即原有内容会被删除。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件。 |
| wb+ | 以二进制格式打开一个文件用于读写。如果该文件已存在则打开文件,并从开头开始编辑,即原有内容会被删除。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件。一般用于非文本文件如图片等。 |
| a | 打开一个文件用于追加。如果该文件已存在,文件指针将会放在文件的结尾。也就是说,新的内容将会被写入到已有内容之后。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件进行写入。 |
| ab | 以二进制格式打开一个文件用于追加。如果该文件已存在,文件指针将会放在文件的结尾。也就是说,新的内容将会被写入到已有内容之后。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件进行写入。 |
| a+ | 打开一个文件用于读写。如果该文件已存在,文件指针将会放在文件的结尾。文件打开时会是追加模式。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件用于读写。 |
| ab+ | 以二进制格式打开一个文件用于追加。如果该文件已存在,文件指针将会放在文件的结尾。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件用于读写。 |
Sequence file processing
- To store records in binary file, we can use module
pickle.
|
|
- You need to import the module.
- Read/write a
file objectvia the binary mode (mode='wb'/'rb'/etc.)
Code example
|
|
Some file fuctions
| 序号 | 方法及描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 关闭文件。关闭后文件不能再进行读写操作。 |
| 6 | 从文件读取指定的字节数,如果未给定或为负则读取所有。 |
| 7 | 读取整行,包括 "\n" 字符。 |
| 8 | 读取所有行并返回列表,若给定sizeint>0,返回总和大约为sizeint字节的行, 实际读取值可能比 sizeint 较大, 因为需要填充缓冲区。 |
| 9 | 移动文件读取指针到指定位置 |
| 10 | 返回文件当前位置。 |
| 11 | 从文件的首行首字符开始截断,截断文件为 size 个字符,无 size 表示从当前位置截断;截断之后后面的所有字符被删除,其中 windows 系统下的换行代表2个字符大小。 |
| 12 | 将字符串写入文件,返回的是写入的字符长度。 |
| 13 | 向文件写入一个序列字符串列表,如果需要换行则要自己加入每行的换行符。 |
Exception



Code language
Pseudocode
|
|
|
|
- TRY
- EXCEPT
- FINALLY - The statements (
<statementsC>) in this block will be executed regardless of whether there was an exception or not.
Python3
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
