Chapter 22: Artificial Intelligence (AI)
An overview
- It is not easy to define ‘Artificial Intelligence’. A key issue is the definition of intelligence.
- a vague definition is best.
- For example: Artificial Intelligence is concerned with
“how to make computers do things at which, at the moment, people are better.”(E. Rich. Artificial Intelligence. McGraw-Hill, 1983)
How graphs can be used in AI
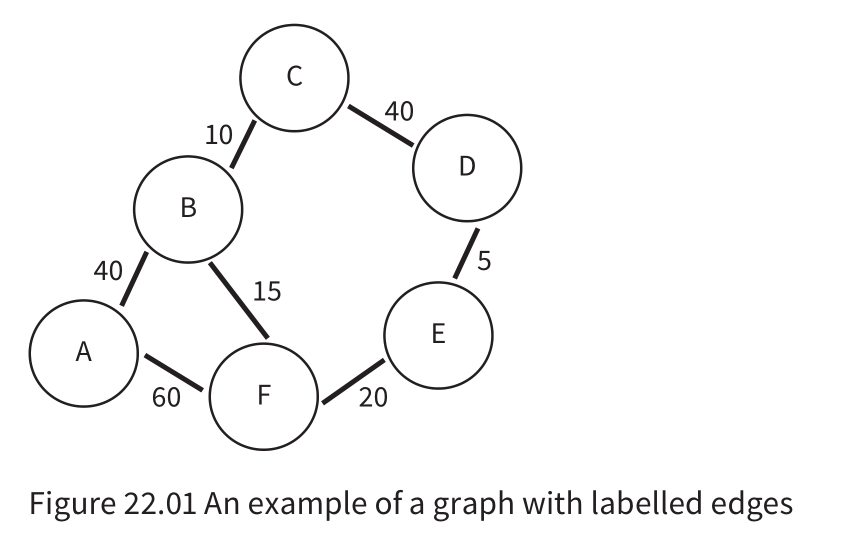
Dijkstra’s algorithm
- Dijkstra’s algorithm is a method of finding the shortest path between two points on a graph. Each point on the graph is called a node or a vertex. It is the basis of technology such as GPS tracking and, therefore, is an important part of AI.
Breif description

Example of graphs
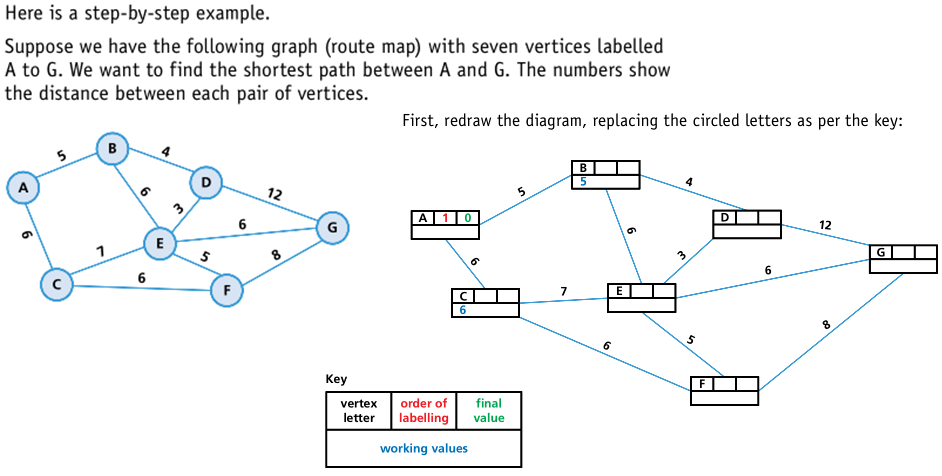
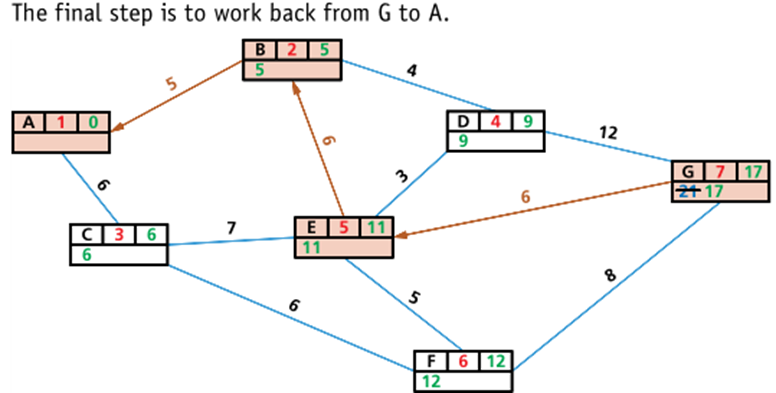
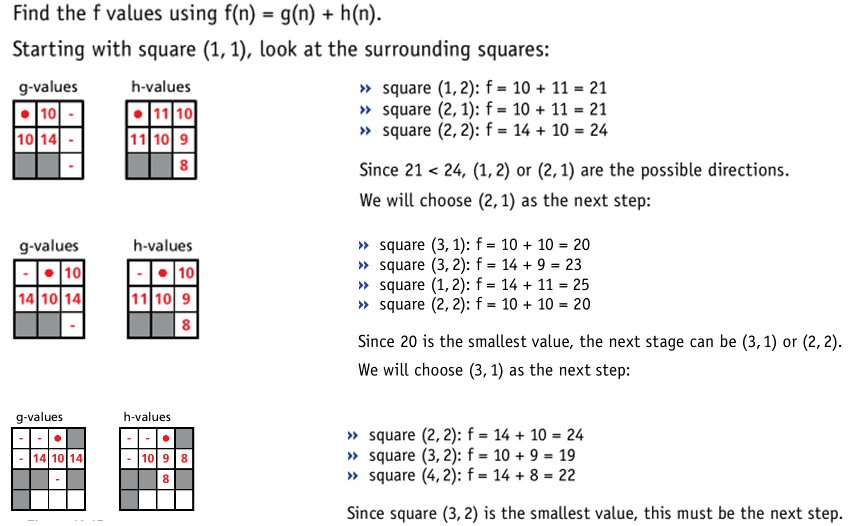
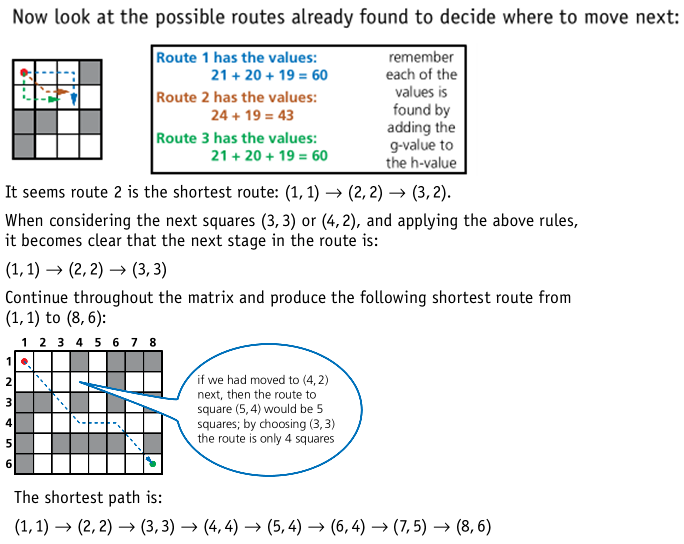
A* algorithm
- The A* algorithm is a modification of the Dijkstra algorithm designed to improve matters. It’s based on Dijkstra, but adds an extra heuristic (h) value – an ‘intelligent guess’ on how far we have to go to reach the destination most efficiently.
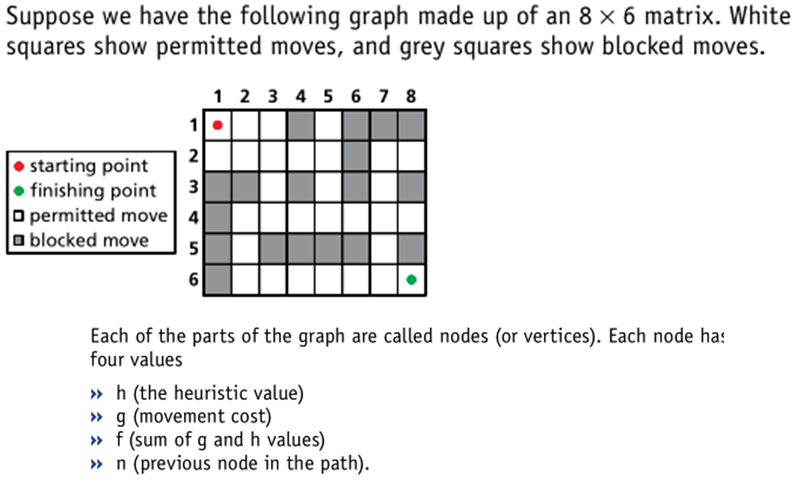


Uses of finding shortest path

Related concepts
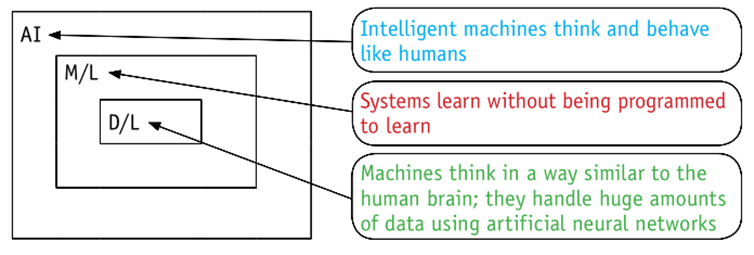


Machine learning
- Machine learning: where a system improves its performance through analysis of previous performance
- Requirements
- A computer-based system has a defined task or tasks to perform
Knowledge is acquired through the experience of performing the tasks- As a result of this experience and the knowledge gained the performance of future tasks is
improved.
- The ability to learn from experience is an indication of intelligence.
Three types of learning
Unsupervised learning
- where the machine learning takes place entirely through the system analysing and categorising the available data

Supervised learning
- where sample data is supplied to the system with associated data relating to the outcome of its use

Reinforcement learning
- where an agent learns by receiving graded rewards for actions taken

Regression analysis methods 回归分析
- Regression analysis: finding a mathematical function that provides the best fit to the actual outcomes when outcomes are calculated from previous inputs

Deep learning
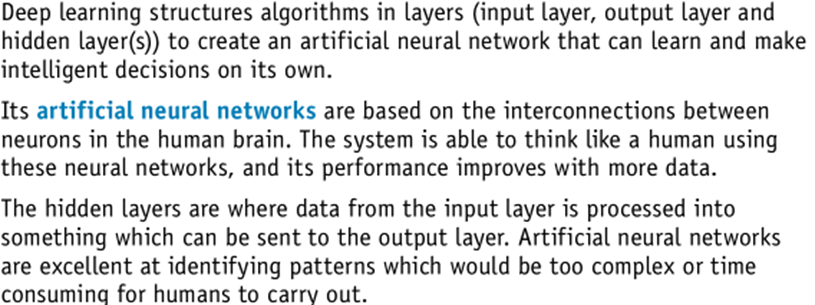
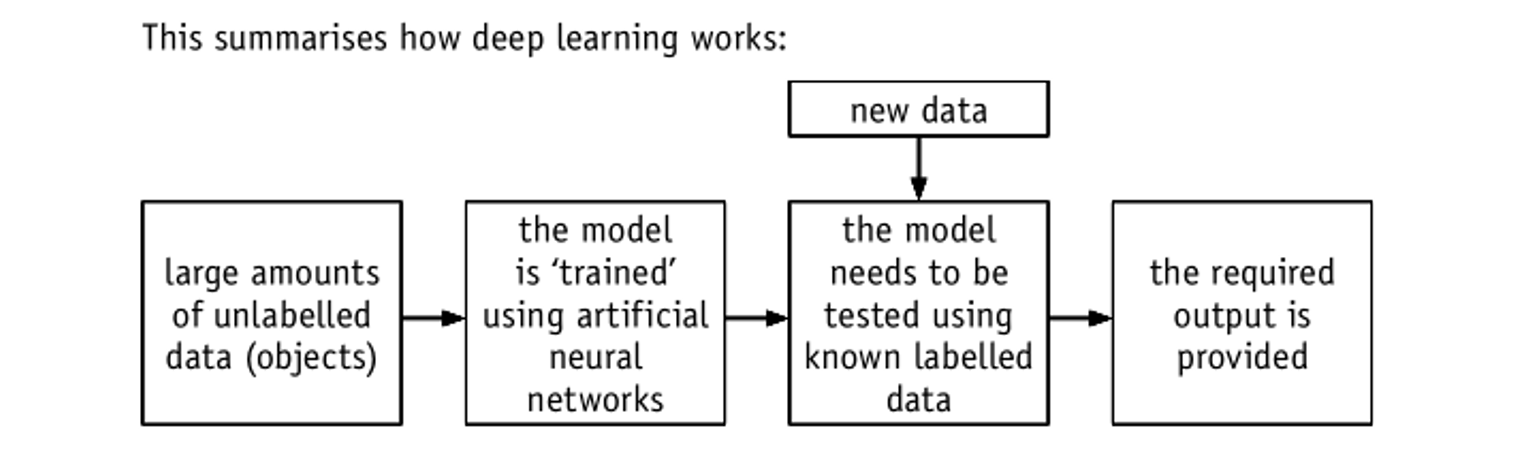
Artificial neural networks
The neural networks in our brains provide our intelligence. It therefore seems obvious that artificial neural networks should be considered as a foundation for artificial intelligence systems.
- Creating a system that functions along similar lines to the way that the human brain works
- Nodes represent artificial neurons
- Nodes are arranged in layers
- A node can adjust the weighting applied to its inputs
- Back propagation of errors is used
- A deep learning system requires many layers
Back propagation of errors
- An algorithm for machine learning that optimises the values for parameters which are adjustable. It is applied first to the nodes in the output layer and then works backward through the nodes in hidden layers until finally the input nodes are considered.

Exam-style Questions
-
Complete the table below to record the progress of the algorithm by identifying which nodes are in the ShortestPath set and what would be stored in the record at each step of the algorithm. Start from A.
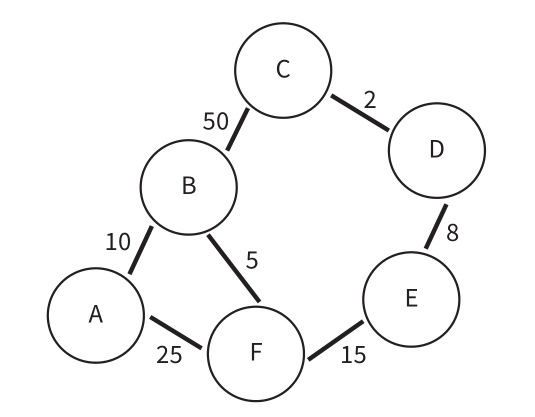
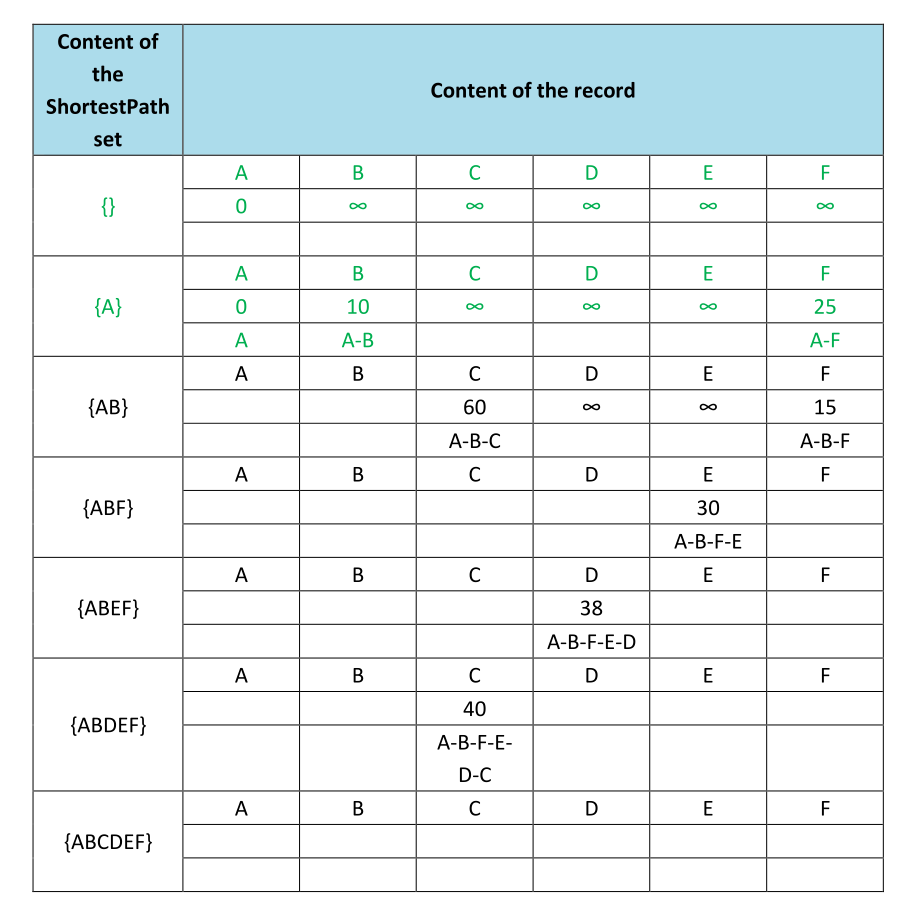 (Green’s word means already given)
(Green’s word means already given) -
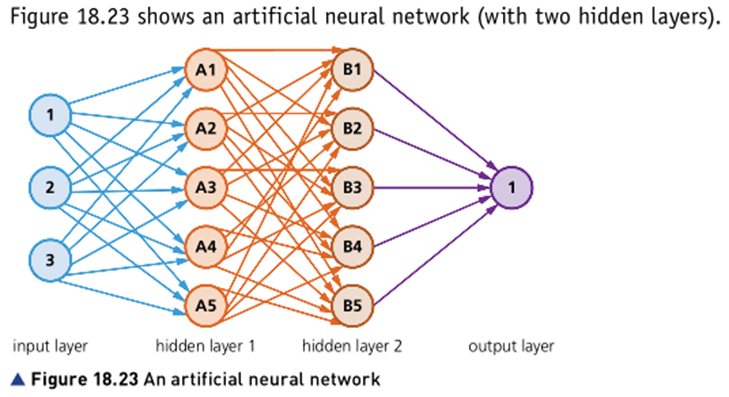
The diagram below represents an artificial neural network.
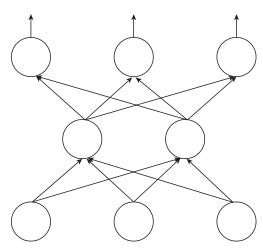
-
Give as full a description as you can of what the parts of the diagram represent. If you wish you can label the diagram then use the labels in your answer. [5]
- The arrows represent data being transferred.
- All nodes except the input nodes receive data from more than one node.
- The nodes that receive input from more than one other node apply a weighting to each input.
- The weighted values are summed.
- The sum is used to calculate an output using an activation function.
-
Identify the steps involved when a backward propagation of errors algorithm is used. [4]
- There must be some actual data available for checking the output from the system (1).
- The aim is to adjust all variable parameters to get the best match with the real data (1).
- In back propagation of errors this begins with the parameters used by the output nodes (1).
- Then, the same happens successively backwards starting from the topmost layer of hidden nodes (1) and finishing with the input nodes (1).
- Give a brief explanation of each of the following terms:
-
Machine learning [3]
- In machine learning a system has a task or tasks to perform (1) for which the level of success can be judged (1).
- Depending on the level of success the system can adjust its methods (1) to improve its performance (1).
- The learning can be supervised or unsupervised (1).
-
Artificial neural network [3]
- An artificial neural network is modelled on how the human brain works (1)
- the system contains nodes that are artificial neurons (1), which can receive input from other nodes or from outside of the system (1)
- and can create an output (1) that depends on the inputs (1) and an activation function (1).
-
Deep learning [3]
- Deep learning is based on an artificial neural network (1)
- has many hidden layers (1)
- the highest-level hidden layers (1) are responsible for more abstract processing (1) in an attempt to match the behaviour of the human brain (1).
-
Explain which approach uses back propagation of errors. [2]
- The artificial neural network (1) can use back propagation of errors because of the layering of the nodes (1) so that parameters can be adjusted in a systematic way (1).