Chapter 19: Logic circuits and Boolean algebra
Logic circuits
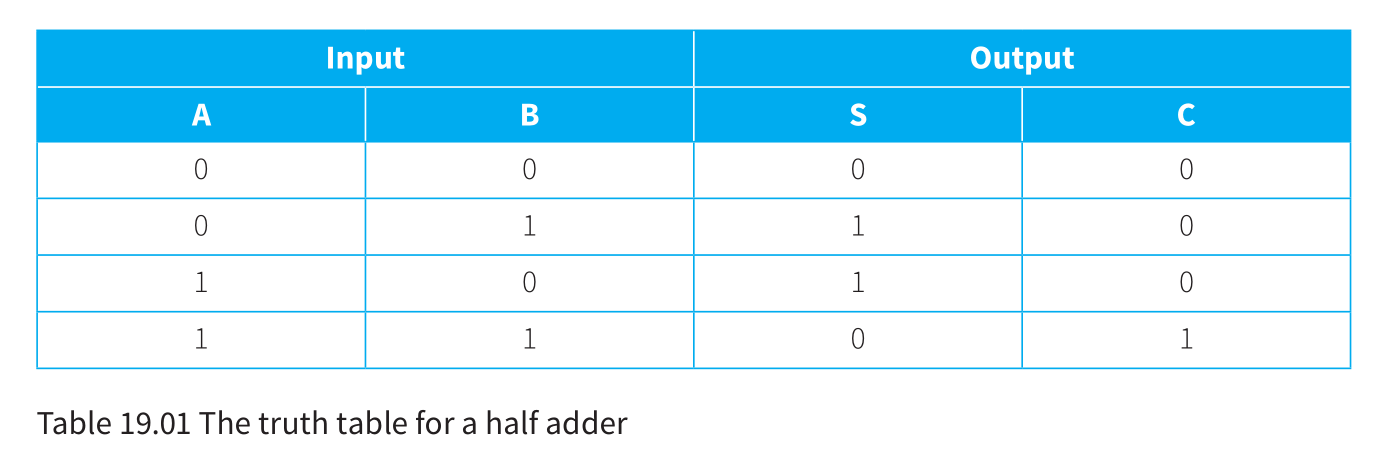
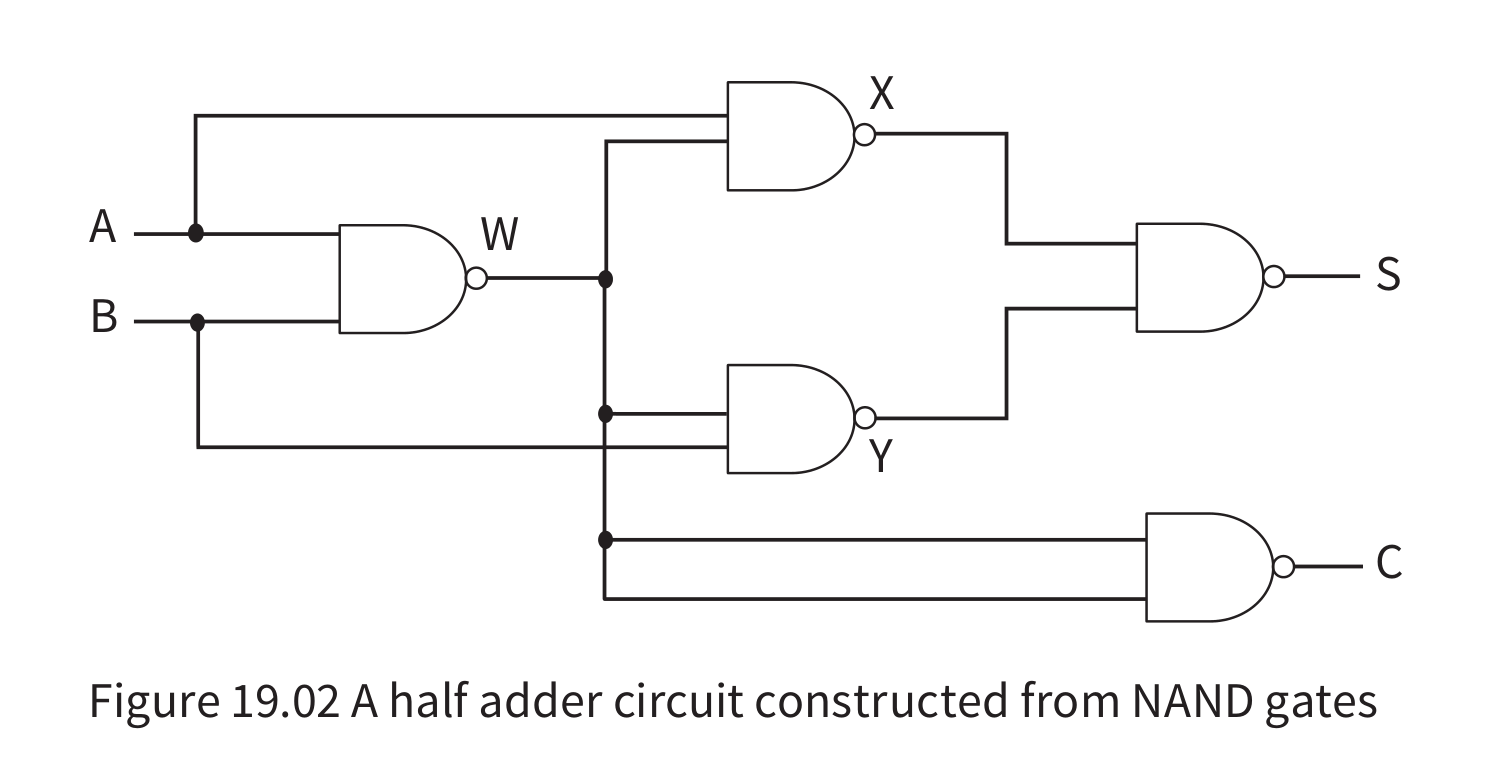
The half adder
- a circuit which performs binary addition of two individual bits
- The simplest circuit that can be used for binary addition is the half adder. This can be represented by the diagram in Figure 19.01. The circuit takes two input bits and outputs
a sum bit (S)anda carry bit (C).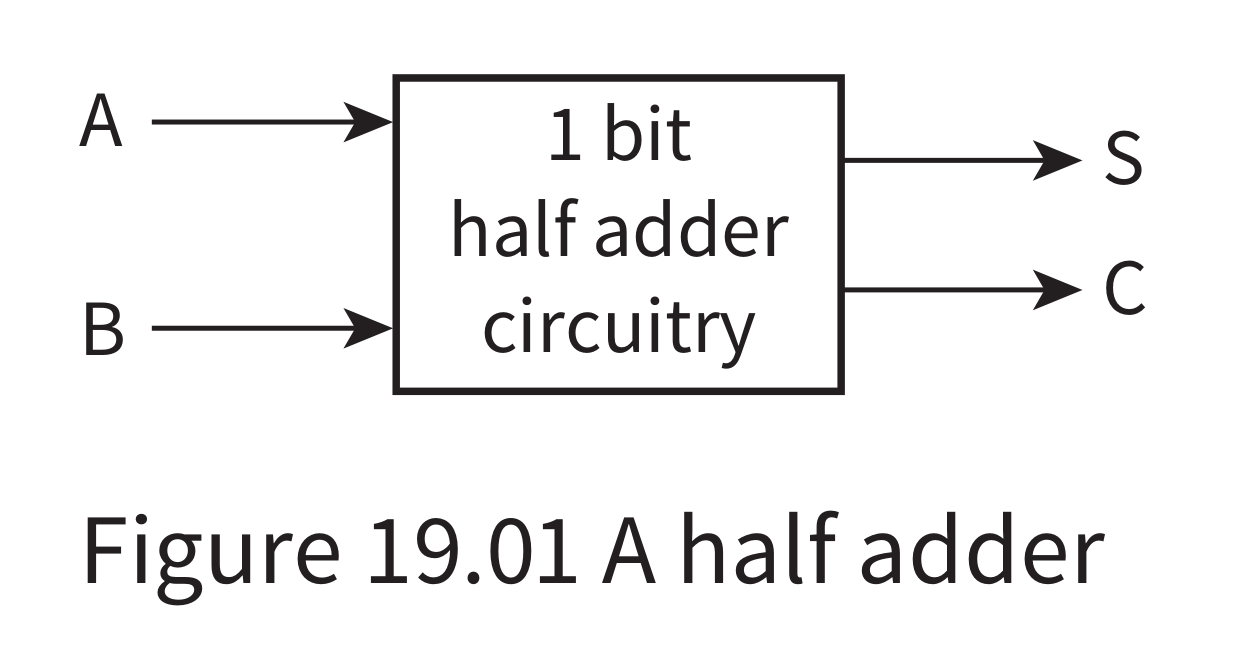
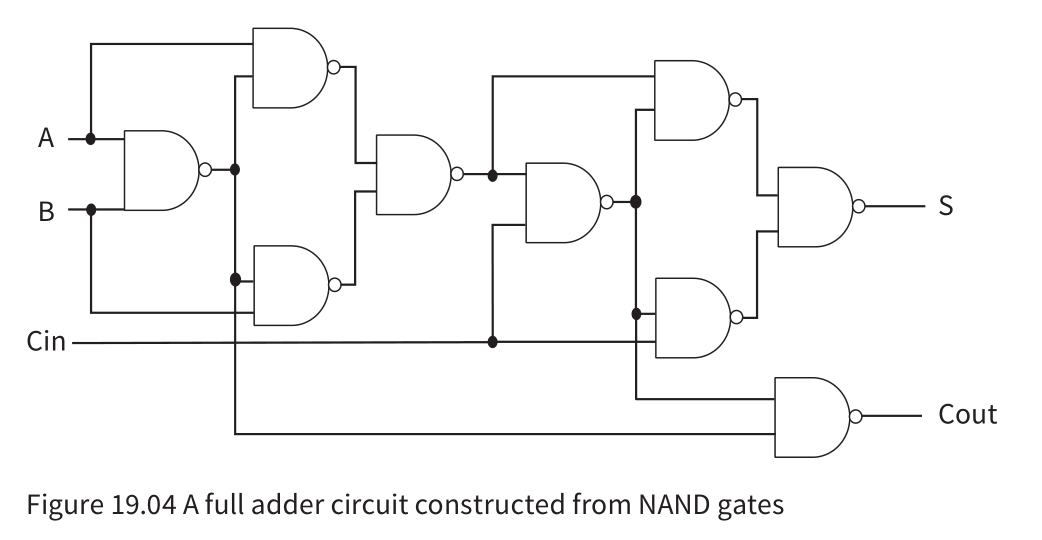
The full adder
- The full adder is a circuit that has three inputs including the previous carry bit.
- a circuit which performs binary addition of two individual bits and an input carry bit
Sequential logic circuits
- Combinational circuit: a circuit in which the output is dependent only on the input values
- Sequential circuit: a circuit in which the output depends on the input values and the previous output
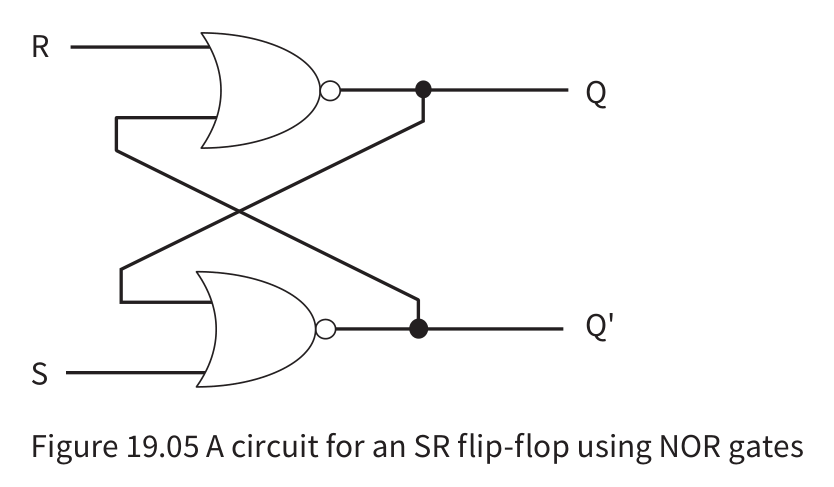
The SR flip-flop
- It can be constructed with two NAND gates or two NOR gates.
- Used as a storage device for 1 bit in the RAM, since it’s values can be altered
- Issue: When the both the input signals are 1 (invalid state) the flip-flop sets the value of Q and Q’ to 0.
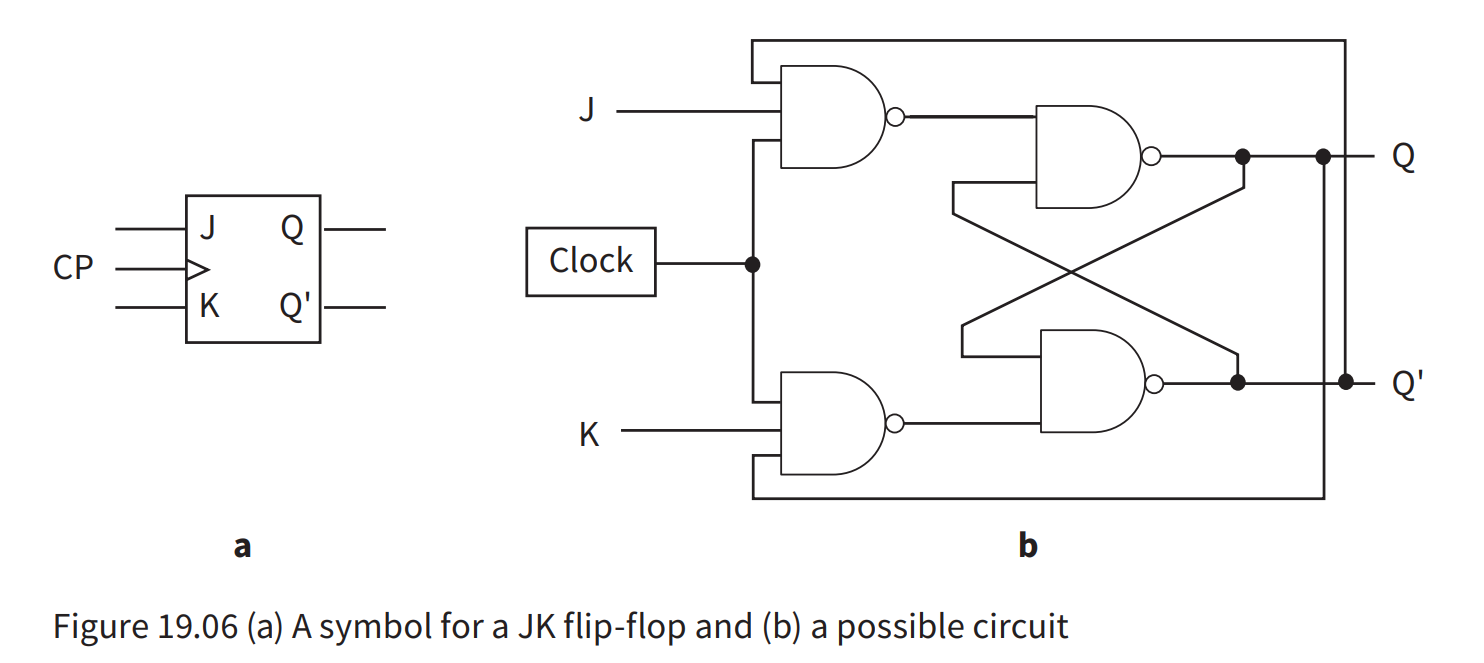
The JK flip-flop
- The J acts as a set input and the K as a clear input.
- In addition to the possibility of entering an invalid state there is also the potential for a circuit to arrive in an uncertain state if inputs do not arrive quite at the same time.
- Fixes the issue with the SR flip-flop by means of a clock input to synchronise the inputs
- When both the input signals are one, Q toggles.
Flip-flops are used to build
- Data storage elements
- Digital circuits
Boolean algebra basics
- 1represents TRUE
- 0 represents FALSE
- . represents AND
- + represents OR
- Ā represents NOT A
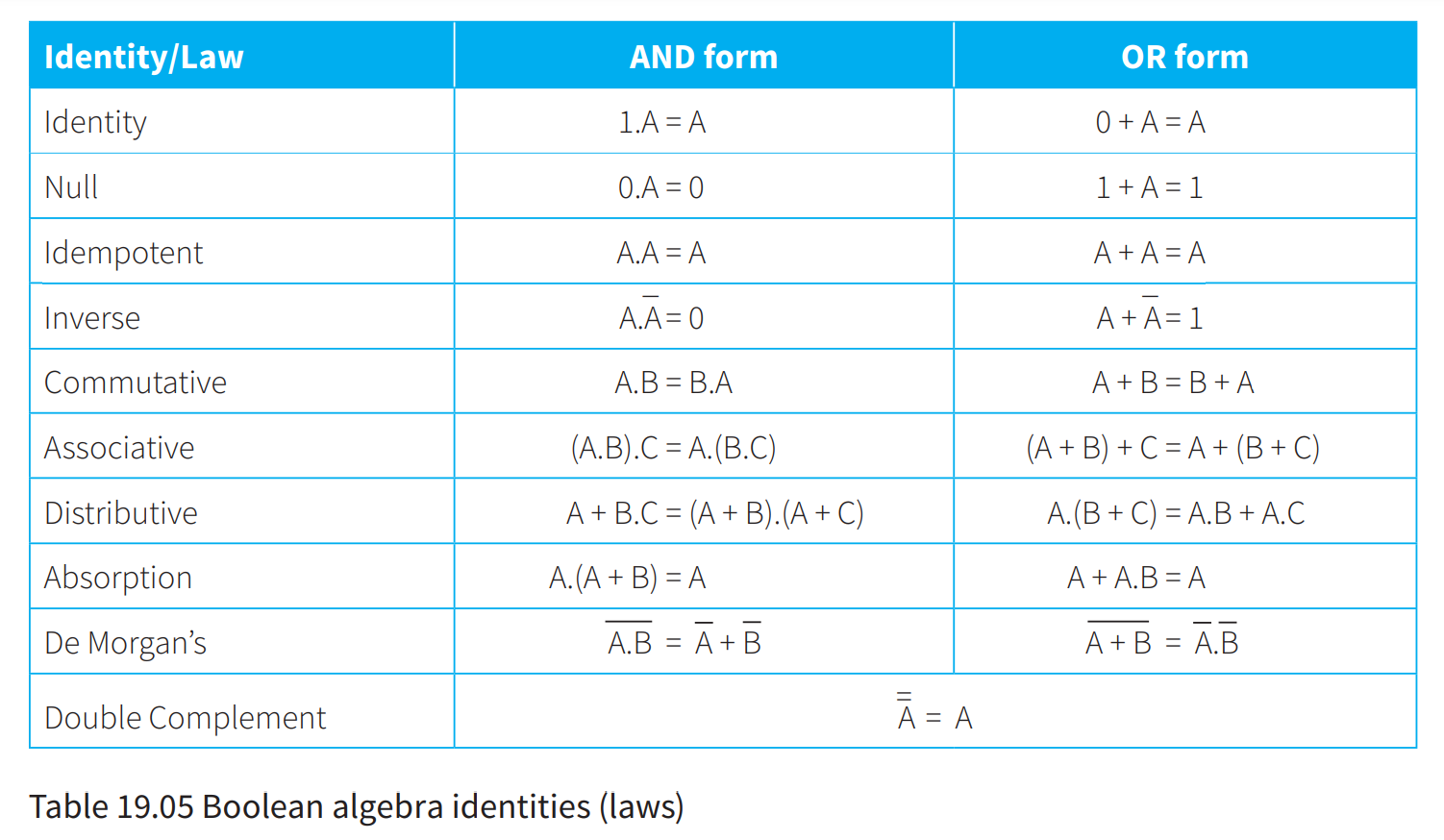
- A + Ā.B can be simplified to A + B
Boolean algebra applications
Creating a Boolean algebra expression directly from a truth table
The Boolean algebra representation of a logic circuit
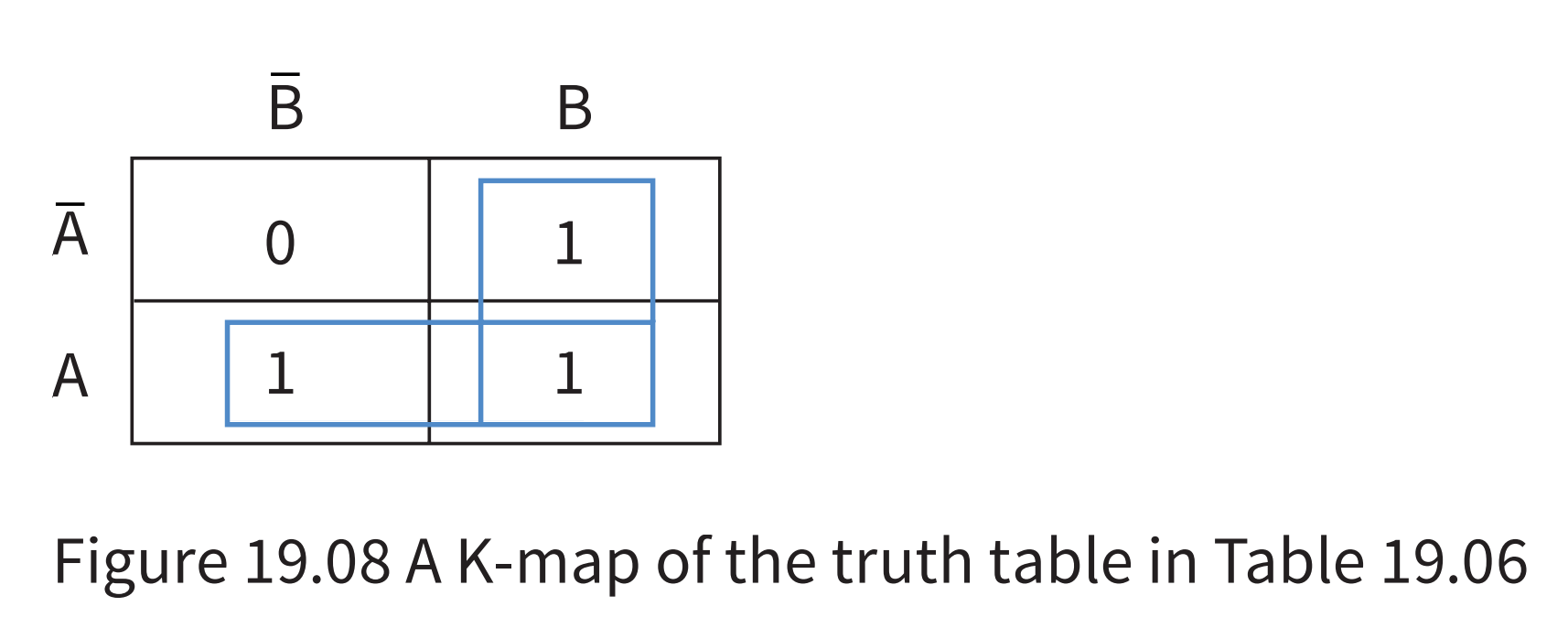
Karnaugh maps (K-maps)
- A Karnaugh map is a method of creating a Boolean algebra expression from a truth table.
- The sum of products method produces the following expression:
|
|
- This is not instantly recognisable as A + B but, with a little effort, using Boolean algebra laws it could be shown to be the same.
- The Karnaugh map approach is simpler. The corresponding K-map is shown in Figure 19.08.
- Each cell in a Karnaugh map shows the value of the output X for a combination of input values for A and B.
K-maps in Chinese description
卡诺图(karnaugh map)
基本知识:
· 卡诺图是由美国工程师卡诺(Karnaugh)首先提出的一种用来描述逻辑函数的特殊方格图。
· 在这个方格图中,每一个方格代表逻辑函数的一个最小项,而且几何相邻(在几何位置上,上下或左右相邻)的小方格具有逻辑相邻性,即两相邻小方格所代表的最小项只有一个变量取值不同。
· 对于有 n 个变量的逻辑函数,其最小项有 2^n 个。因此该逻辑函数的卡诺图由 2^n 个小方格构成,每个小方格都满足逻辑相邻项的要求。
稍微整理下上面的基本知识点:
-
一种描述逻辑函数特殊方格图。
-
每格代表一个最小项,上下左右相邻就具备相邻性。
-
有 n 个变量,最小项就有 2^n 且卡诺图也由 2^n 个格子构成。
两变量的卡诺图:
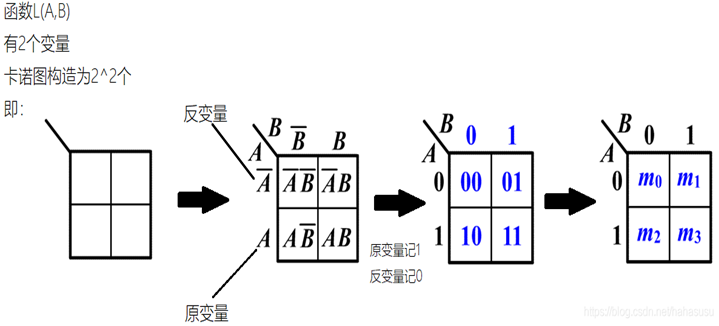
三变量的卡诺图:
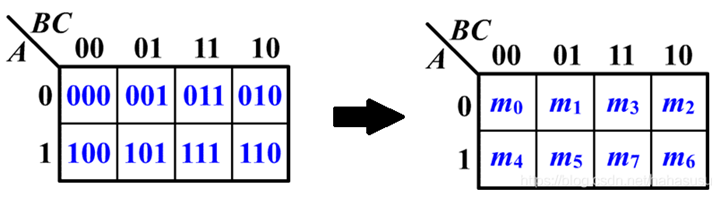
四变量的卡诺图以此类推吧!
**例 2:**画出逻辑函数的卡诺图。
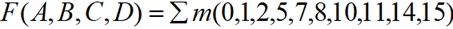
解:
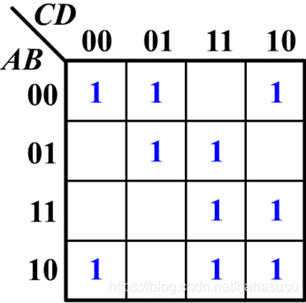
通过上面的例子,我们已经掌握如何画卡诺图,接下来就是如何使用卡诺图进行化简。
3.逻辑函数的卡诺图化简法
卡诺图相邻性的特点保证了几何相邻两方格所代表的最小项只有一个变量不同。因此,若相邻的方格都为 1(简称 1 格)时,则对应的最小项就可以合并。合并的结果是消去这个不同的变量,只保留相同的变量。这是图形化简法的依据。
综上所述,卡诺图具备以下特性:
-
卡诺图中两个相邻 1 格的最小项可以合并成一个与项,并消去一个变量。
-
卡诺图中四个相邻 1 格的最小项可以合并成一个与项,并消去两个变量。
-
卡诺图中八个相邻 1 格的最小项可以合并成一个与项,并消去三个变量。
利用这 3 点特性来接着看下面的例子:
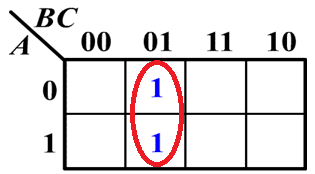
上图两个相邻 1 格的最小项可以合并成一个与项,并消去一个变量,化简式子如下:
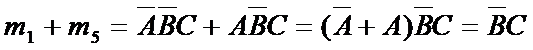
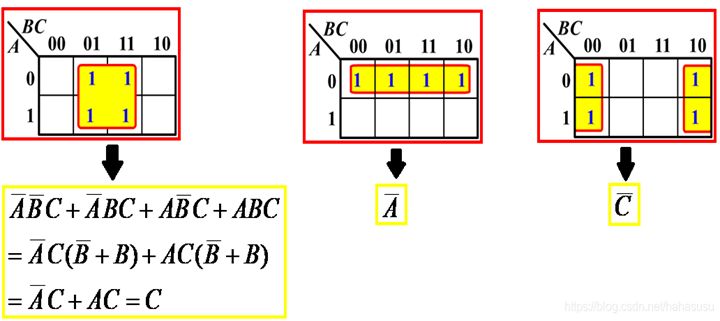
根据上面 3 个特性再来看几个例子加深理解,以下是 4 个相邻 1 格的:
再来看一题:
用卡诺图化简法求最简与或表达式
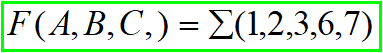
先画出卡诺图,然后转换十进制对应 1,2,3,6,7 的地方填入为 1,其余填写为 0(这个步骤有前面的知识点支撑,应该不难理解了。)
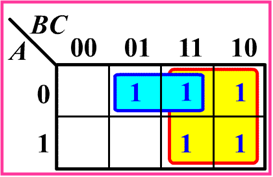
然后获得式子:F =(m1+m3)+(m2+m3+m6+m7)
即:
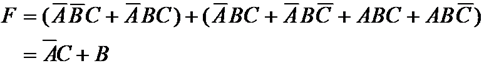
好了到此,我们已经清楚如何化简了,接下来是对如何对卡诺图进行画圈进行探讨。
首先,有这么几点需要明确:
-
列出逻辑函数的最小项表达式,由最小项表达式确定变量的个数(如果最小项中缺少变量,应按例的方法补齐)。
-
画出最小项表达式对应的卡诺图。
-
将卡诺图中的 1 格画圈,一个也不能漏圈,否则最后得到的表达式就会与所给函数不等;1 格允许被一个以上的圈所包围。
-
圈的个数应尽可能得少。即在保证 1 格一个也不漏圈的前提下,圈的个数越少越好。因为一个圈和一个与项相对应,圈数越少,与或表达式的与项就越少。
-
按照 2k 个方格来组合(即圈内的 1 格数必须为 1,2,4,8 等),圈的面积越大越好。因为圈越大,可消去的变量就越多,与项中的变量就越少。
-
每个圈应至少包含一个新的 1 格,否则这个圈是多余的。
-
用卡诺图化简所得到的最简与或式不是唯一的。
带着这 7 点来看
例 3:用卡诺图化简以下表达式
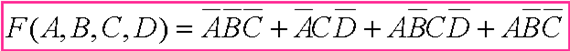
解: 从表达式中可以看出此为四变量的逻辑函数,但是有的乘积项中缺少一个变量,不符合最小项的规定。因此,每个乘积项中都要将缺少的变量补上:
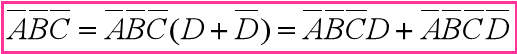
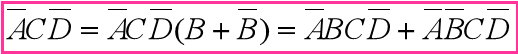
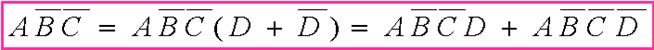
因此,获得整个表达式如下:
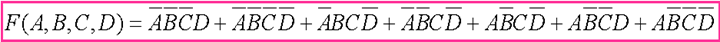
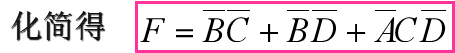
这里演示了刚才提示的(1)点,最小项缺少变量补齐。
例 2:
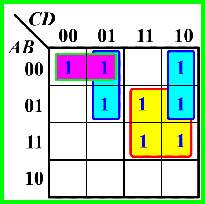
错误 (多画一个圈)
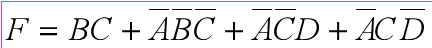
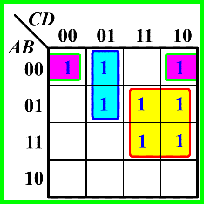
正确
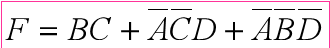
例 3:
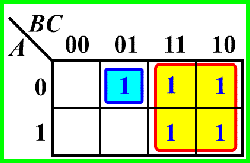
错误(圈的面积不够大)
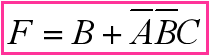
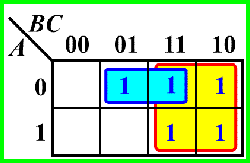
正确
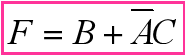
例 4:
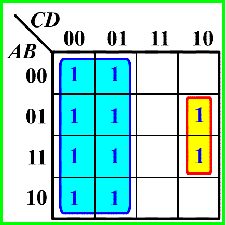
错误(圈的面积不够大)
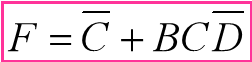
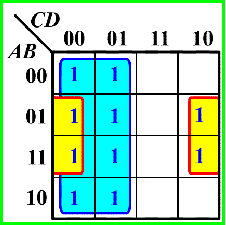
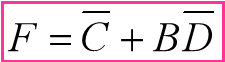
例 5:
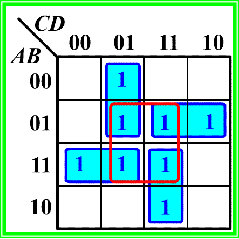
错误(有一个圈无新的 1 格)
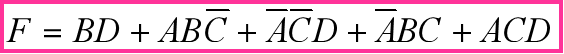
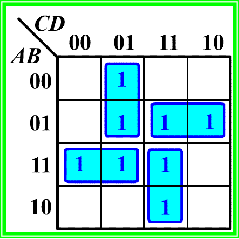
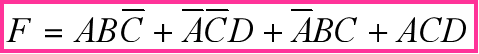
到此为止,你已经学会了如何利用卡诺图化简法来化简函数。