Chapter 18: Hardware and virtual machines
The control unit
- Control unit within the CPU to ensure that each machine instruction is handled correctly
- There are two methods by which a control unit can be designed to allow it to perform its function. - One method is for the control unit to be constructed as a
logic circuit. This is called thehard-wired solution. The machine-code instructions are handled directly by hardware. - The alternative method is for the control unit to usemicroprogramming. In this approach, the control unit contains aROM componentthat stores the microinstructions or microcode for microprogramming, often referred to as firmware.
CISC and RISC processors
- Instruction set architecture - the instruction set - the instruction format - the addressing modes - the registers accessible by instructions.
- Complex Instruction Set Computer (CISC): a single instruction can be more complex and involve more loading of data from memory
- Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC): a single instruction is simpler, requiring minimal loading of data from memory
| RISC | CISC |
|---|---|
| Fewer instructions | More instructions |
| Simpler instructions | More complex instructions |
| Small number of instruction formats | Many instruction formats |
| Single-cycle instructions whenever possible | Multi-cycle instructions |
| Fixed-length instructions | Variable-length instructions |
| Only load and store instructions to address memory | Many types of instructions to address memory |
| Fewer addressing modes | More addressing modes |
| Multiple register sets | Fewer registers |
| Hard-wired control unit | Microprogrammed control unit |
| Pipelining easier | Pipelining more difficult |
Pipelining
- Pipelining: instruction-level parallelism | From coursebook
- 指令层级平行(Instruction-level parallelism,缩写为 ILP,也译为指令级并行),一种并行计算形式,在一个程序运行中,许多指令操作,能在同时间进行。它也是一个测量值,用来计算在一个程序运算中,它有多少个指令能够在同时间运算,称为指令层级平行度。 | From wiki
The basic computer architectures
- To describing different
computer architecturesis to considerthe number of instruction streamsandthe number of data streams.
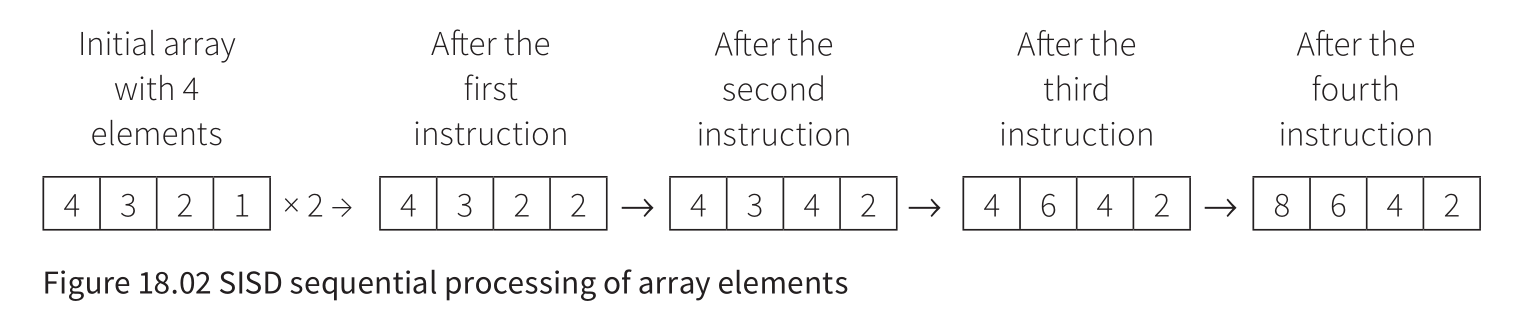
Single Instruction Stream Single Data Stream (SISD)
- sequential with no parallelism
- a single processor accessing one memory
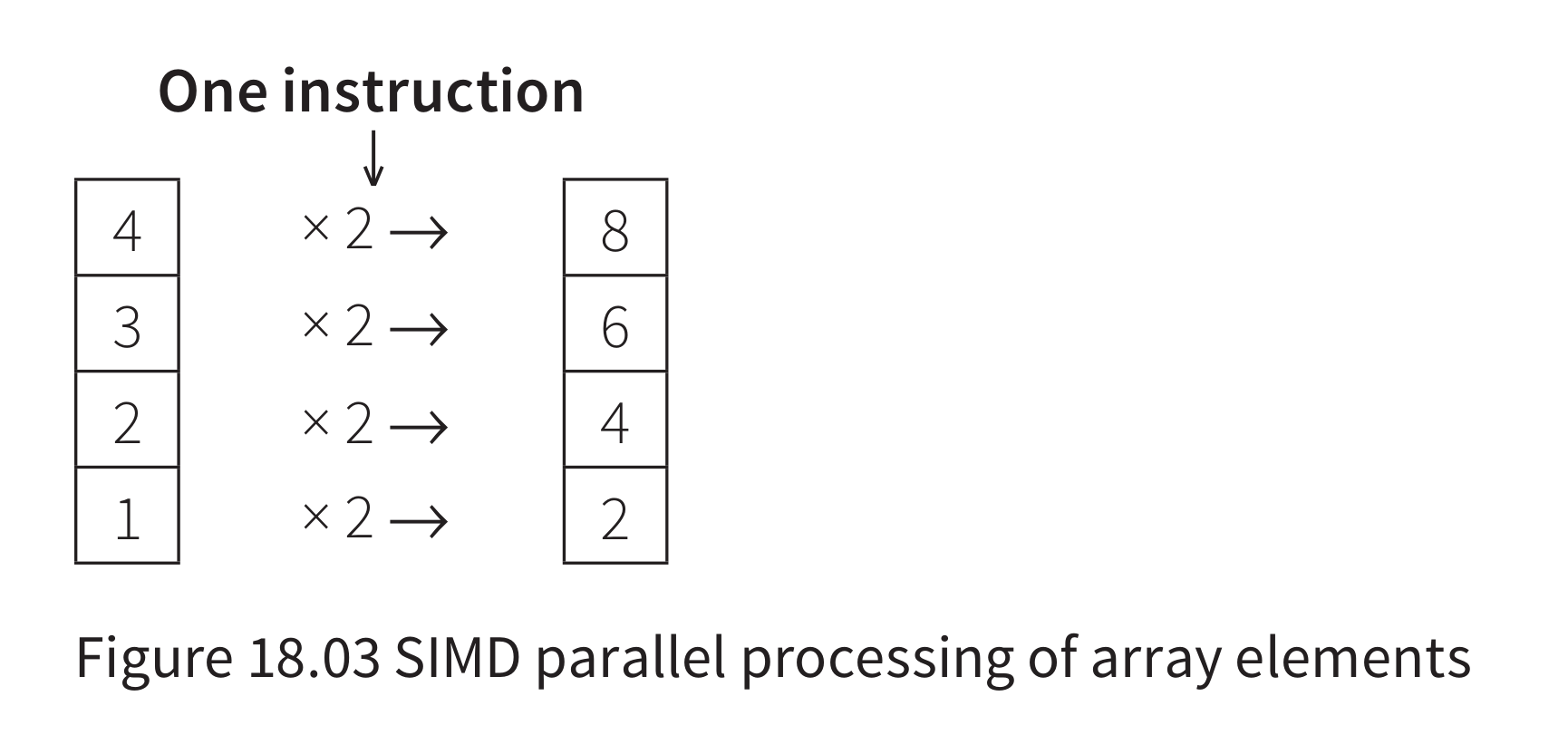
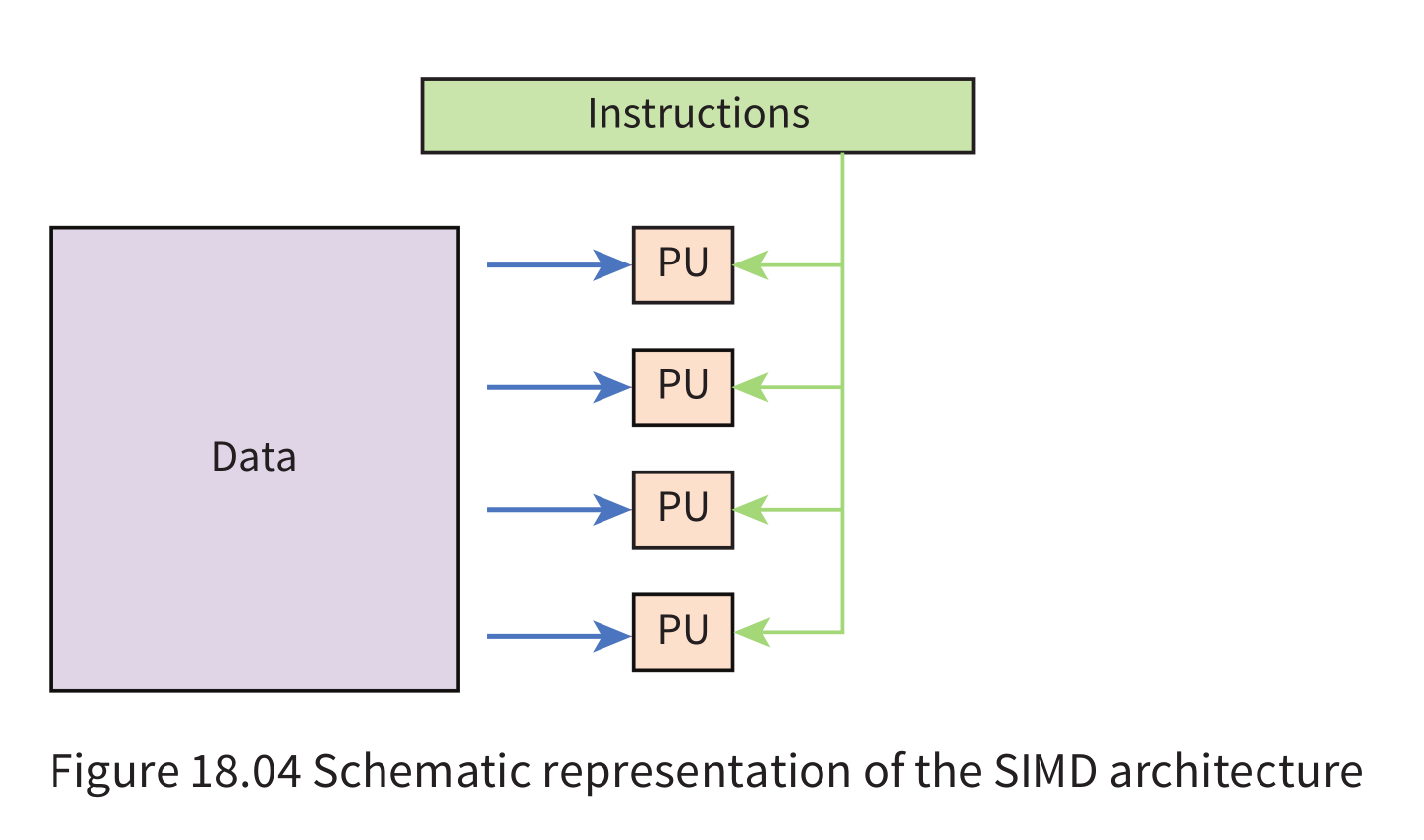
Single Instruction Stream Multiple Data Stream (SIMD)
- processing of parallel data input requiring one
control unit instructing multiple processing units
Multiple Instruction Stream Single Data Stream (MISD)
- MISD is not evidenced in any individual computer architecture design.
Multiple Instruction Stream Multiple Data Stream (MIMD)
- multiple processors asynchronously processing parallel data input
Massively parallel computer systems (大规模并行处理计算机)
- The MIMD architecture can be implemented in multicomputer systems known as massively parallel computers.
- These are the systems used by large organisations for computations involving highly complex mathematical processing.
- These systems have an extremely large number of individual
processors working in parallel.
Virtual machines
- System virtual machine: the emulation of computer system hardware using software
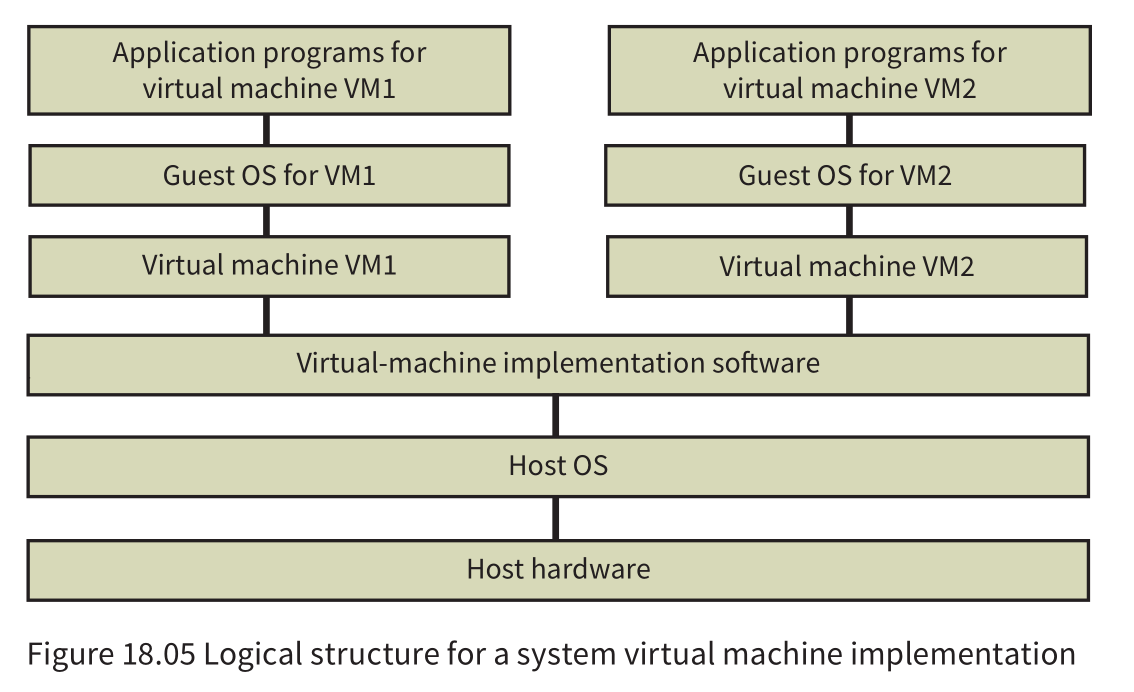
- The application programs are installed with the assistance of a guest OS. This guest OS will support the running application by interacting with the virtual machine as though it were the hardware that the guest OS would normally run on.
- The virtual machine implementation software can be considered to be a utility program which, when running, is supported by the particular host OS which is specific to the host hardware.
- There can be application programs running at the same time directly on the host hardware under the control of the host OS.
- Advantages
- More than one different operating system can be made available on one computer system.
- Continue to use the old software but does not wish to keep the old hardware.
- Drawbacks
- To using a virtual machine is the time and effort required for implementation.
- The implementation will not offer the same level of performance that would be obtained on a normal system.
JVM
The Java virtual machine is an example of a process virtual machine, based on a different underlying concept. The process virtual machine provides a platform-independent programming environment that allows a program to execute in the same way on any platform. This is specific software that only supports running a Java program. A system virtual machine supports any application.
Description of Java in AS CS
When the programming language Java was created, a different philosophy was applied to how it should be used. Each different type of computer has to have a Java Virtual Machine created for it. Then when a programmer writes a Java program this is compiled first of all to create what is called Java Byte Code. When the program is run, this code is interpreted by the Java Virtual Machine. The Java Byte Code can be transferred to any computer that has a Java Virtual Machine installed.